Thirty-four years ago, astronomer and Cosmos host Carl Sagan made his famous claim:
“If you wish to make an apple pie from scratch, you must first invent the universe.” – Carl Sagan. “The Lives of the Stars.” Cosmos: A Personal Voyage. PBS. 1980.
Sagan could have been talking about making anything from scratch. His goal was to convey that everything on earth, everything in the universe, is made up of precise combinations of the most basic elements, and those elements were created in stars’ nuclear cores. We could also say, “If you wish to make a pot from scratch, you must first invent the universe.”
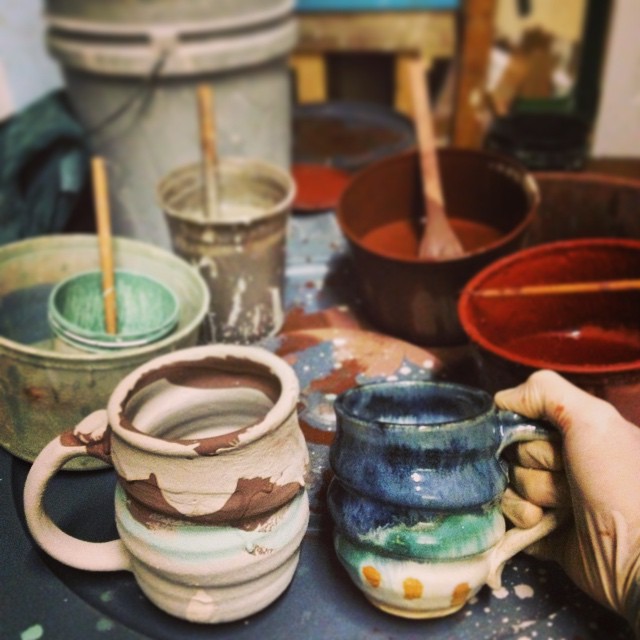
These star-forged elements combine to form all the components of ceramics: the different strains of clay (silicon and iron), the water used in throwing (oxygen and hydrogen), the arboreal ingredients of glazes (calcium), and even the potter himself (carbon). Entire books could be written focusing solely on one of these ceramic elements.
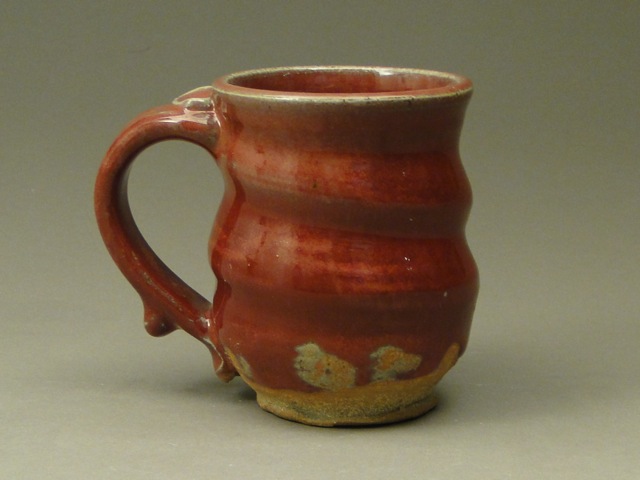
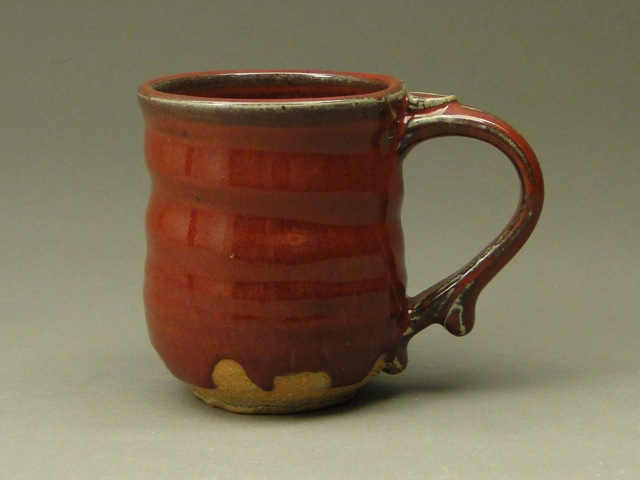
 Copper, for example. Copper red glazes have been meticulously pursued and produced since the fifteenth century in China. The new host of Cosmos, Neil deGrasse Tyson, often analyzes the concept of a “Goldilocks planet” – a planet which has the precise conditions for possibly sustaining life. A successful copper red glaze is a “Goldilocks glaze.” Everything in both the recipe and the firing must be perfect.
Copper, for example. Copper red glazes have been meticulously pursued and produced since the fifteenth century in China. The new host of Cosmos, Neil deGrasse Tyson, often analyzes the concept of a “Goldilocks planet” – a planet which has the precise conditions for possibly sustaining life. A successful copper red glaze is a “Goldilocks glaze.” Everything in both the recipe and the firing must be perfect.
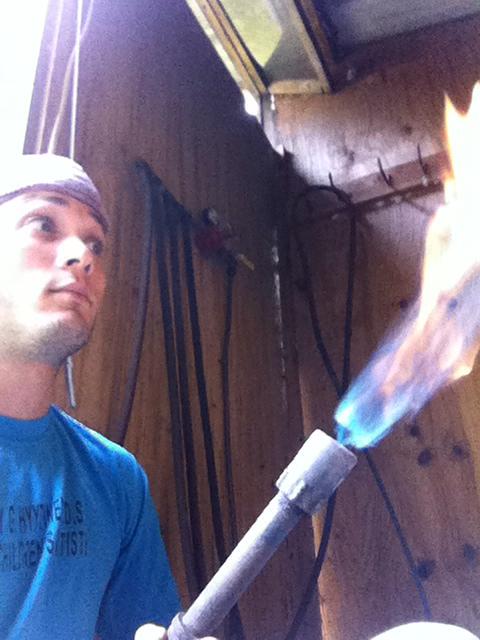

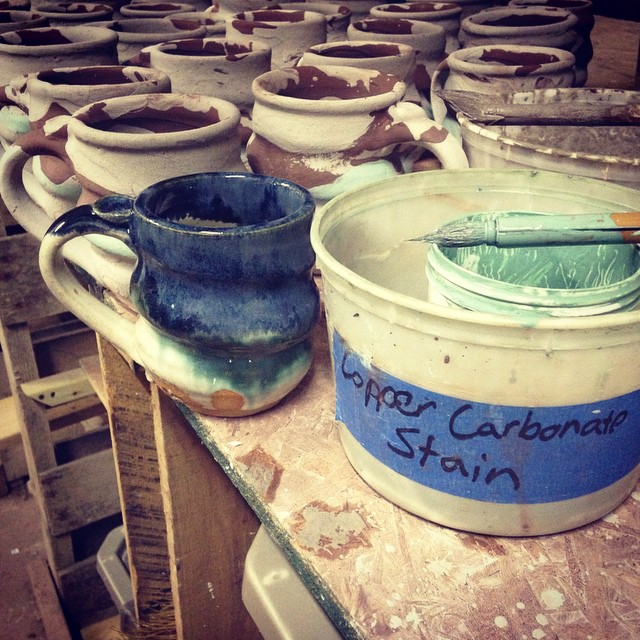
As Sagan and Tyson have taught us, science is found in everything we do. Baking an apple pie from scratch, developing a new drug, and mixing and firing glazes all rely on experimentation, creativity, and chemical reactions. A potter doesn’t need a degree in chemistry, but he uses some pretty cool science to produce copper red glazes.
 Nowadays, gas-fired kilns produce the best conditions for copper red glazes, but ancient Chinese potters created their beautiful pieces using only wood-fired kilns. Many potters do not have regular access to gas- or wood-fired kilns, and use electric ones instead. Electric kilns eliminate the need for constant temperature monitoring, but they are unable to create the atmosphere copper red glazes require.
Nowadays, gas-fired kilns produce the best conditions for copper red glazes, but ancient Chinese potters created their beautiful pieces using only wood-fired kilns. Many potters do not have regular access to gas- or wood-fired kilns, and use electric ones instead. Electric kilns eliminate the need for constant temperature monitoring, but they are unable to create the atmosphere copper red glazes require.
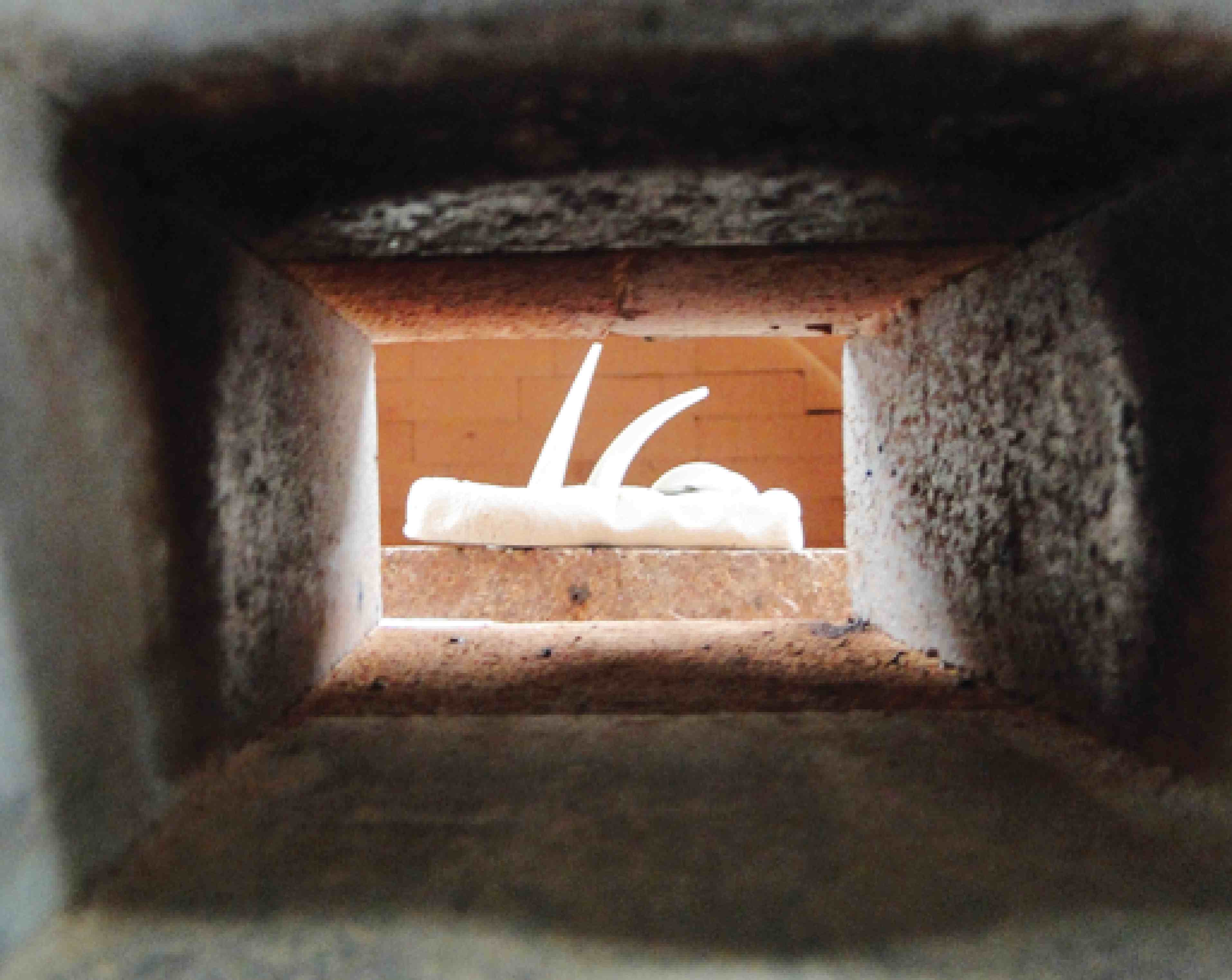

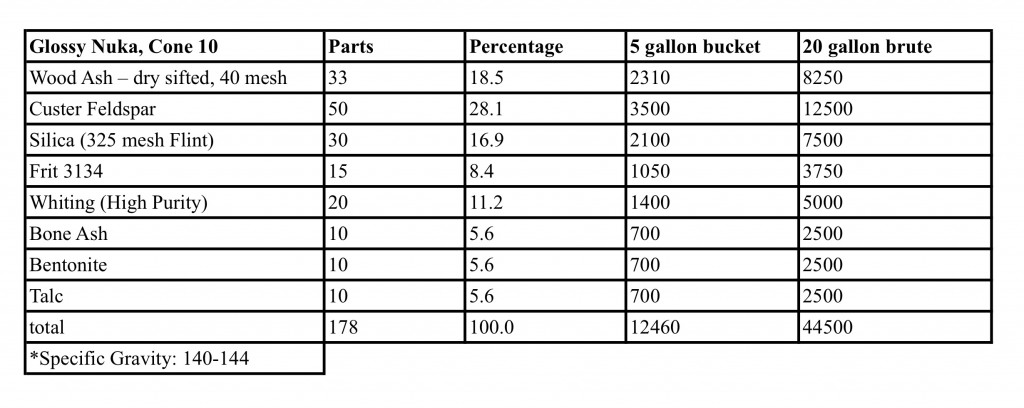
Copper red glazes need to be fired to a temperature called “cone 10.” This photo shows three cones (small pieces of clay), set up inside a gas-fired kiln. Each of these pieces is made from a different factory-produced type of clay formulated to melt at a certain temperature. A device called a pyrometer can be used to measure the temperature of the air inside the kiln, but what really matters is the temperature of the clay, hence the use of cones. When cone 10 melts, the potter knows the clay is roughly 2345 °F.
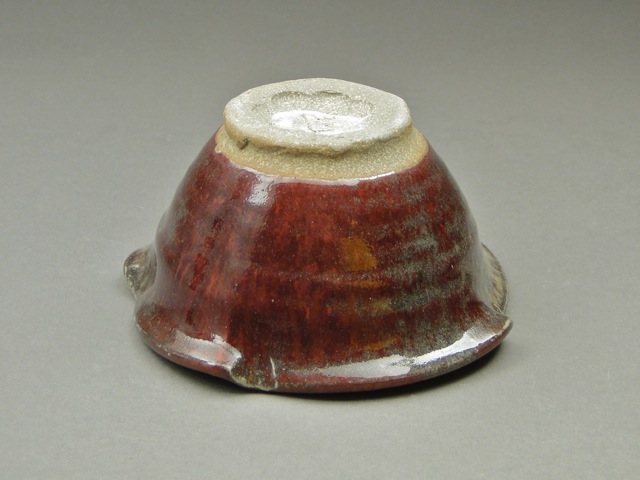
 Even inside the same kiln, the atmosphere unavoidably varies. The pots below all had the same glaze and firing, but were placed in different areas of the kiln.
Even inside the same kiln, the atmosphere unavoidably varies. The pots below all had the same glaze and firing, but were placed in different areas of the kiln.
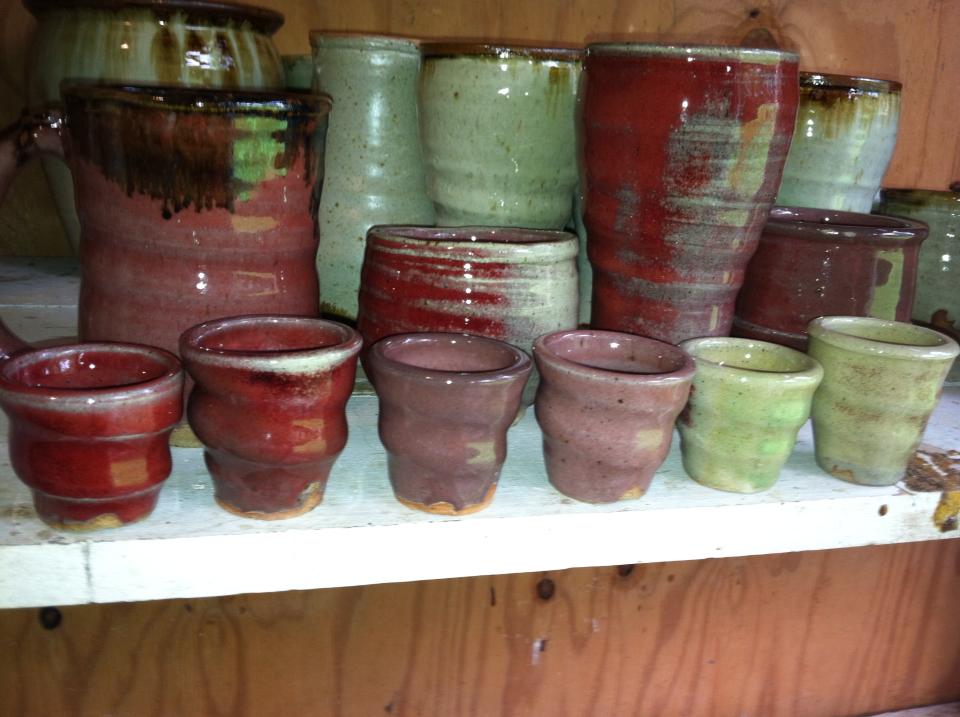 The green color on the right also occurs when firing a copper glaze in an electric kiln.
The green color on the right also occurs when firing a copper glaze in an electric kiln.
Color, just like copper, depends on the stars. Light from our sun strikes objects on earth, and those objects absorb some wavelengths of light and reflect others. The wavelengths they reflect are the colors we see. As Tyson puts it:
“Color is the way our eyes perceive how energetic light waves are.” – Neil Degrasse Tyson. “Hiding in the Light.” Cosmos: A Spacetime Odyssey. Fox. 2014.
Thankfully, potters did not have to create the universe to make pots from scratch. Their ingredients are already present in the cosmos, swirling in the air and lurking in the earth, waiting for them.